
Allogenic mesenchymal stem cell therapy (completed phase IV clinical trials)
A novel patented technology achieved from harvesting multiple bone marrow donors, ex-vivo cultured, and then pooled together to obtain human adult bone marrow derived allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells used for therapeutic purposes. The pooling method balances out variations observed when using individual donor cells, resulting in a product with strong immune-modulatory properties, broader cytokine / growth factors array, longer lifespan and consistent clinical outcomes. It is available as 'off-the-shelf' cryopreserved stem cell product.
Now, higher number of viable cells is now achievable due to unique cryopreservation solution which ensure the cells are not losing their multi-potent differentiation ability and cytokine production capacity after thawing.

Stempeucel is the FIRST innovative stem cell-based available off-the shelf biological product that has been granted approval by DCGI (Indian FDA) for marketing and commercialization of the treatment of Critical Limb Ischaemia, Peripheral arterial disease and osteoarthritis.
Chronic Limb Ischaemia (CLI)
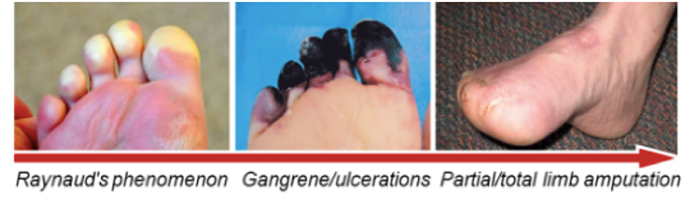
A non-atherosclerotic , segmental inflammatory disease that affects small and medium-sized arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities. The disease progresses to critical limb Ischaemia (CLI) and manifest as rest pain, uncurable ulceration, gangrene, lost of toes or limb often leading to limb amputation.
CLI due to Buerger's Disease
Inflammation and clotting caused by severe obstruction of arteries which markedly reduces blood flow to the extremities (hands, feet and legs). CLI (BD) is different from CLI (PAD – Peripheral Arterial Disease) because unlike PAD, it is not caused by accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques
Commonly seen in younger smokers/ tobacco users (20-40 years of age), mostly male. Most common symptoms are rest pain, ulcers and gangrene
CLI due to Peripheral Arterial Disease
Critical Limb Ischemia disease characterized by narrowing of arteries in the legs limiting blood flow to the muscles due to atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of the arteries over time due to the buildup of fatty deposits called plaque
Causes include smoking, diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol, high blood pressure or age related factors. Serious condition that requires immediate treatment to re-establish blood-flow to the affected area to preserve the limb from amputation
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Phase III safety and efficacy trials, off-the-shelf, allogeneic, cultured, pooled, human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cell ("MSC"). OA is being developed for the treatment of Osteoarthritis ("OA") of the knee joint.
Overview of Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. It develops gradually over time and most commonly affects the hands, knees, hips, feet and spine.
In OA affected cartilage, the cartilage breaks down, causing pain and friction between exposed bone. OA then worsens to form bone spurs. Bits of bone or cartilage may chip off and float around in the joint and lead into Inflammatory stage, which will then further damage the cartilage.
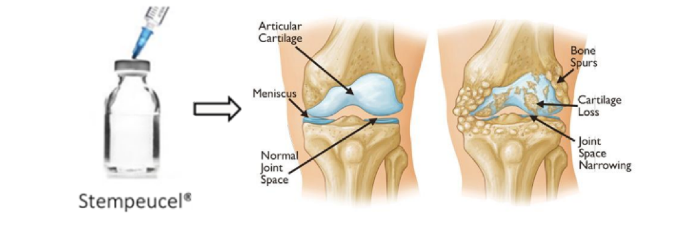
Stempeucel® has the potential to reduce the pain for a longer period of time compared to HA, thus delaying the need for knee replacement surgery.
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
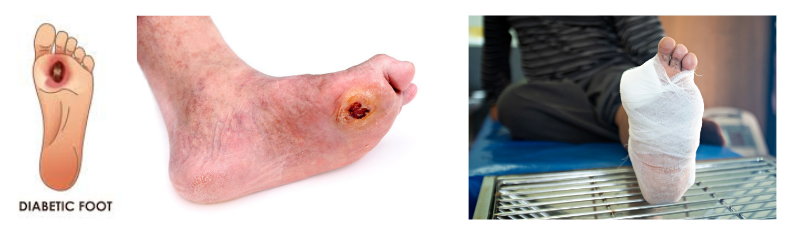
Diabetes resulted in delayed wound healing due to impairment in the inflammation and angiogenesis mechanism. Diabetic ulcer most commonly happened in the foot, which is a leading cause to lower extremity amputation. MSCs is known to regulate inflammation and angiogenesis via secretion of various growth factors and cytokines that were involved in both mechanisms. DCGI has approved the phase 3 clinical trial for diabetic foot ulcer whereby 84 patients were divided equally to receive Stempeucel® and placebo. Study was done across India consisting of 17 hospitals. Stempeucel® injection in and around the wound bed, demonstrates accentuation of the healing process and reduction of the ulcer area.
